The RuM laboratory develops technologies that enable computerized systems to perceive the world, interpret it, make decisions, and act. We believe that robotics, artificial perception, and artificial intelligence will play an increasingly important role in human development, both in everyday life, industry and economy, as well as politics. EDI RuM’s goal is to become a significant player in shaping this future. A player whose research results and developed technologies are not only valued in their scientific field but also promote human welfare, safety, and health. So far, we have developed and adapted our laboratory technologies for various applications in the fields of medicine, industry, agriculture, and mobility.
Keywords:
- machine learning, deep neural networks, synthetic training data
- artificial intelligence – explainable, generative, physics-informed
- automation, industrial robots, real-time control, mobile robots
- embedded intelligence and computer vision
- program synthesis
The laboratory consists of four research groups – three of which focus on different aspects of artificial intelligence and one specializes in robotics research.
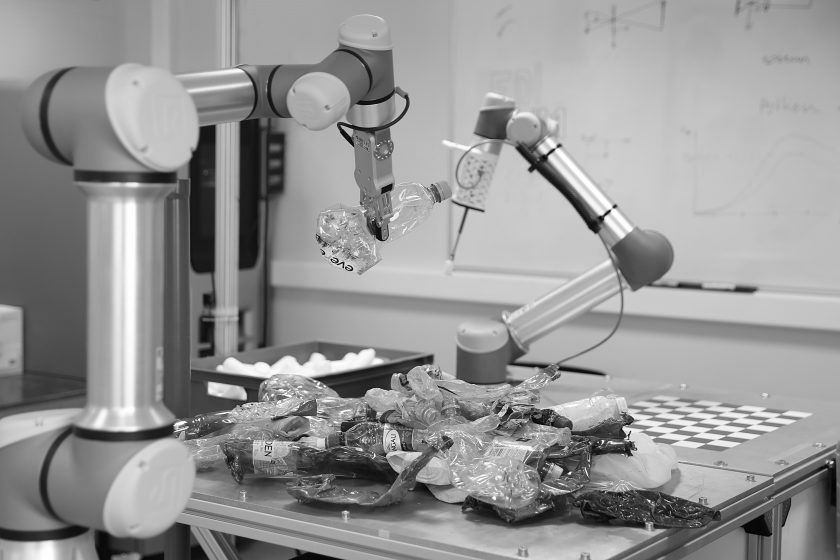
The robotics group led by Ph.D. Jānis Ārents has long-term goals aimed at enabling robots to operate effectively in complex, unstructured environments and interact seamlessly with humans. To achieve this, our work is focused on developing fundamental autonomous mobile navigation capabilities in unstructured environments, as seen in projects like VIZTA, EdgeAI, and MOTE, which explore the use of computer vision and other sensor modalities for perception and semantic scene interpretation. The main goal is to equip robots with the ability to perform general-purpose manipulation and interaction, as illustrated by our work in industrial manipulation within TRINITY and IMOCO4.E, as well as our efforts to facilitate robot-human interaction through projects like AI4DI. This involves not only enhanced perception but also the development of high-level reasoning and task execution, where projects like EdgeAI focus on parsing natural language instructions and grounding them in environmental context using compact, interpretable AI models. Furthermore, we are committed to integrating advanced perception and sensors, including unconventional modalities, with projects like MOTE and EdgeAI adapting open-ended semantic perception to real-world conditions and real-time constraints, allowing for rapid integration of new observations and task-specific information extraction, such as traversable ground segmentation. Our work in recent years, including the development of semantic scene interpretation (MOTE), natural language grounding (EdgeAI), and human interaction (AI4DI), has directly contributed to these goals, enabling robots to understand and operate in open, dynamic environments. We have also focused on developing perception systems that can operate effectively under real-world conditions and real-time constraints, as demonstrated in MOTE and EdgeAI, and creating planning systems that can understand natural language instructions and ground them in the environment using efficient AI models, which is a key aspect of EdgeAI. With these ongoing efforts, we are shaping a future where robots can operate autonomously and collaboratively across a wide range of complex real-world scenarios.
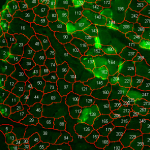
Dr. sc. comp. Kaspars Sudars’ group aims to develop better artificial intelligence that leads to scientific excellence, as well as develop AI-based technology that leads to commercialization opportunities. The main theme of the group is explainable artificial intelligence and its methods. In this direction, the group researches fundamental AI models for intelligent system development and uses explainable artificial intelligence to identify relevant data features responsible for AI decision-making. Explainable AI is particularly important in healthcare applications, for which the group has conducted national grant projects OSTAK and LU-AIDA. The group also trains deep neural network models in various industry applications with a high technology readiness level (TRL).
The general scientific direction of the group led by Dr. sc. comp. Kārlis Freivalds is machine learning and artificial intelligence. An additional direction is the creation and application of various mathematical algorithms and the creation of innovative devices based on mathematical algorithms. The most important application currently is in robotics, for example within the international project AIMS5.0. Additionally, the group works with fundamental artificial intelligence topics – physics-informed AI and program synthesis.
The laboratory head Dr. sc. ing. Roberts Kadiķis’ group works on solving computer vision tasks (object detection, image classification, and segmentation) using both machine learning methods and classical image processing approaches. A significant research area is generative AI (generative adversarial networks, diffusion models), which we use for generating synthetic training data. For example, within the ERDF project AimOOC, generative AI was used to synthesize images of organs cultivated on chips, which were then used to train image classifiers for automating the cultivation process. The group actively seeks new applications for generative AI, resulting in solutions such as virtual medical image staining (LZP project HAVeT-AI) and making 3D modelled synhtetic data look more like real images. Models whose perception capabilities have been enhanced with various data synthesis and data augmentation methods are further applied in mobile systems (projects COMP4DRONES, Augmented CCAM), industrial robot systems (VIZTA IMOCO4.E), and for medical image analysis.
Recent projects
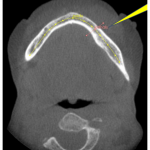
- Interpretable AI-Powered System for Identification of Bone Metastases in Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (A.I.B.M.)
- Soil biological quality index (QBS) determination using machine learning (QBS) #LZP FLPP
-
 Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing leading to Sustainability and Industry 5.0 (AIMS5.0) #ChipsJU
Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing leading to Sustainability and Industry 5.0 (AIMS5.0) #ChipsJU
-
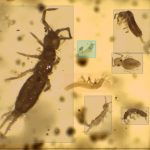
 Holographic microscopy- and artificial intelligence-based digital pathology for the next generation of cytology in veterinary medicine (VetCyto) #ChipsJU
Holographic microscopy- and artificial intelligence-based digital pathology for the next generation of cytology in veterinary medicine (VetCyto) #ChipsJU
-
 Histological recognition and analysis of veterinary tumors surgical margins by using artificial intelligence and multimodal imaging (HAVeT-AI ) #ChipsJU
Histological recognition and analysis of veterinary tumors surgical margins by using artificial intelligence and multimodal imaging (HAVeT-AI ) #ChipsJU
-
 Augmenting and Evaluating the Physical and Digital Infrastructure for CCAM deployment (AUGMENTED CCAM) #Horizon Europe
Augmenting and Evaluating the Physical and Digital Infrastructure for CCAM deployment (AUGMENTED CCAM) #Horizon Europe
-
 Edge AI Technologies for Optimised Performance Embedded Processing (EdgeAI) #ChipsJU
Edge AI Technologies for Optimised Performance Embedded Processing (EdgeAI) #ChipsJU
-
 A Deep Learning Approach for Osteoporosis Identification using Cone-beam Computed Tomography (OSTAK) #ChipsJU
A Deep Learning Approach for Osteoporosis Identification using Cone-beam Computed Tomography (OSTAK) #ChipsJU
- AI-improved organ on chip cultivation for personalised medicine (AImOOC) #ChipsJU
-
 New technology to produce hydrogen from Renewable Energy Sources based on AI with optimized costs for environmental applications (HydroG(re)EnergY-Env) #ChipsJU
New technology to produce hydrogen from Renewable Energy Sources based on AI with optimized costs for environmental applications (HydroG(re)EnergY-Env) #ChipsJU
Publications
- Sudars, K., Namatevs, I., Nikulins, A., & Ozols, K. (2025). Privacy Auditing of Lithium-Ion Battery Ageing Model by Recovering Time-Series Data Using Gradient Inversion Attack in Federated Learning. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5704.
- Tomass Zutis, Peteris Racinskis, Anzelika Bureka, Janis Judvaitis, Janis Arents, and Modris Greitans. Multi-Step Object Re-Identification on Edge Devices: A Pipeline for Vehicle Re-Identification.
- Fišere, I.; Edelmers, E.; Svirskis, Š.; Groma, V. Utilisation of Deep Neural Networks for Estimation of Cajal Cells in the Anal Canal Wall of Patients with Advanced Haemorrhoidal Disease Treated by LigaSure Surgery. Cells 2025, 14, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070550
- Arturs Nikulins, Edgars Edelmers, Kaspars Sudars, Inese Polaka. 2025. "Adapting Classification Neural Network Architectures for Medical Image Segmentation Using Explainable AI" Journal of Imaging, 11(2): pp.55. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11020055
- Ivars Namatevs, Kaspars Sudars, Arturs Nikulins, Kaspars Ozols. 2025. "Privacy Auditing in Differential Private Machine Learning: The Current Trends" Applied Sciences, 15(2): 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020647
- Blaz Cugmas, Eva Štruc, Inese Bērziņa, Mindaugas Tamošiūnas, Laura Goldberga, Thierry Olivry, Kārlis Zviedris, Roberts Kadiķis, Maksims Ivanovs, Miran Bürmen, Peter Naglič. "Automated classification of pollens relevant to veterinary medicine" 2024 IEEE 14th International Conference Nanomaterials: Applications & Properties (NAP) https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10739713
- Oskars Vismanis, Janis Arents, Jurga Subačiute-Žemaitieṅe, Vytautas Bučinskas, Andrius Dzedzickis, Brijesh Patel, Wei-Cheng Tung, Po-Ting Lin, Modris Greitans "A Vision-Based Micro-Manipulation System" Applied Sciences 13(24) http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/app132413248
- Peteris Racinskis , Oskars Vismanis , Toms Eduards Zinars , Janis Arents and Modris Greitans "Towards Open-Set NLP-Based Multi-Level Planning for Robotic Tasks" Applied Sciences, 14(22)L pp.10717. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210717
- Edgars Edelmers, Dzintra Kazoka, Katrina Bolocko, Kaspars Sudars, Mara Pilmane, Automatization of CT Annotation: Combining AI Efficiency with Expert Precision
- Edīte Kaufmane, Edgars Edelmers, Kaspars Sudars, Ivars Namatēvs, Arturs Nikulins, Sarmīte Strautiņa, Ieva Kalniņa, Astile Peter. 2023. "Three-Dimensional Imaging in Agriculture: Challenges and Advancements in the Phenotyping of Japanese Quinces in Latvia", Horticulturae, 9(12): pp.16. https://www.mdpi.com/2311-7524/9/12/1347
- Andris Lapins, Janis Arents and Modris Greitans, "Augmenting a Pretrained Object Detection Model with Planar Pose Estimation Capability", Automatic Control and Computer Sciences, 57(5), pp. 459-468, https://link.springer.com/article/10.3103/S0146411623050061
- Ivars Namatēvs, Kaspars Sudars, Artūrs Ņikuļins, Anda Slaidiņa, Laura Neimane, Oskars Radziņš, "Towards Explainability of the Latent Space by Disentangled Representation Learning", Information Technology and Management Science
- Ivars Namatevs, Arturs Nikulins, Edgars Edelmers, Laura Neimane, Anda Slaidina, Oskars Radzins, Kaspars Sudars, "Modular Neural Networks for Osteoporosis Detection in Mandibular Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scans",
- Kaspars Sudars, Ivars Namatevs, Arturs Nikulins, Edgars Edelmers, Laura Neimane, Anda Slaidina, Oskars Radzins, "Artificial Intelligence-Powered System for Identifying Bone Deterioration in Radiological Imaging", International Workshop on Embedded Digital Intelligence (IWoEDI'2023)
- Ivars Namatevs, Kaspars Sudars, Arturs Nikulins, Anda Slaidina, Laura Neimane, Oskars Radzins, Edgars Edelmers, "Denoising Diffusion Algorithm for Single Image Inplaine Super-Resolution in CBCT Scans of the Mandible", 023 IEEE 64th International Scientific Conference on Information Technology and Management Science of Riga Technical University (ITMS)
- Toms Eduards Zinars, Oskars Vismanis, Peteris Racinskis, Janis Arents, Modris Greitans. Natural Language Conditioned Planning of Complex Robotics Tasks. In: Advancing Edge Artificial Intelligence, River Publishers Series in Communications and Networking
- Maksims Ivanovs, Laura Leja, Kārlis Zviedris, Roberts Rimsa, Karina Narbute, Valerija Movcana, Felikss Rumnieks, Arnis Strods, Kevin Gillois, Gatis Mozolevskis, Arturs Abols, Roberts Kadikis. Synthetic Image Generation With a Fine-Tuned Latent Diffusion Model for Organ on Chip Cell Image Classification. Signal Processing - Algorithms, Architectures, Arrangements, and Applications Conference Proceedings, SPA
- Sajid Mohamed, Gijs van der Veen, Hans Kuppens, Matias Vierimaa, Tassos Kanellos, Henry Stoutjesdijk, Riccardo Masiero, Kalle Määttä, Jan Wytze van der Weit, Gabriel Ribeiro, Ansgar Bergmann, Davide Colombo, Javier Arenas, Alfie Keary, Martin Goubej, Benjamin Rouxel, Pekka Kilpeläinen, Roberts Kadikis, Mikel Armendia, Petr Blaha, Joep Stokkermans, Martin Čech, Arend-Jan Beltmans. The IMOCO4.E reference framework for intelligent motion control systems. IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, ETFA, 2023.
- Mindaugas Tamošiūnas, Roberts Kadiķis, Mikus Melderis, Romāns Maļiks, Diāna Duplevska, Daira Viškere, Ilze Matīse-van Houtana, Blaž Cugmas. 2023. "Wide-field Raman spectral band imaging of tumor lesions in veterinary medicine" Translational Biophotonics: Diagnostics and Therapeutics III, 12627: pp. 295-302. https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/12627/1262737/Wide-field-Raman-spectral-band-imaging-of-tumor-lesions-in/10.1117/12.2686917.short
- Kārlis Freivalds, Emīls Ozoliņš, Guntis Bārzdiņš. "Discrete Denoising Diffusion Approach to Integer Factorization" Proceedings of 32nd International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks 2023 , Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS, volume 14254) Part I, pp. 123-134
- Zakovskis, R., Draguns, A., Gaile, E., Ozolins, E., Freivalds, K. (2023). Gates Are Not What You Need in RNNs. In: Rutkowski, L., Scherer, R., Korytkowski, M., Pedrycz, W., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zurada, J.M. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing. ICAISC 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14125. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42505-9_27
- Kaspars Sudars, Ivars Namatevs, Arturs Nikulins, Rihards Balass, Astile Peter, Sarmite Strautina, Edite Kaufmane, Ieva Kalnina "Semantic Segmentation Using U-Net Deep Learning Network for Quince Phenotyping on RGB and HyperSpectral Images", 27th International Conference "Electronics" (2023). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10177638.
- M. Laizans, J. Arents, O. Vismanis, V. Bučinskas, A. Dzedzickis, and M. Greitans. 2023. "Supplementation of synthetic object replicas for increasing precision of microrobot trajectory keypoints" Robotic Systems and Applications, 3(1): pp47-58. https://www.extrica.com/article/23128, http://dx.doi.org/10.21595/rsa.2023.23128
- Oskars Vismanis, Janis Arents, Karlis Freivalds, Vaibhav Ahluwalia and Kaspars Ozols. 2023. "Robotic System for Post Office Package Handling" Applied Sciences 13(13 - Number) 7643 (Article Number), https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/13/13/7643
- Peteris Racinskis, Janis Arents, Modris Greitans. "Constructing Maps for Autonomous Robotics: An Introductory Conceptual Overview, 2023" Electronics 12(13): pp2925, https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/12/13/2925
- Vitalijs Fescenko, Janis Arents and Roberts Kadikis. 2023. "Synthetic Data Generation for Visual Detection of Flattened PET Bottles" Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 5(1), pp14-28. https://www.mdpi.com/2504-4990/5/1/2
- Peteris Racinskis, Janis Arents, Modris Greitans. 2023. (POSTER) Drone Detection and Localization using Low-Cost Microphone Arrays and Convolutional Neural Networks, 2023 19th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Smart Systems and the Internet of Things (DCOSS-IoT), pp.80-82.
- D. Duplevska, V. Medvedevs, D. Surmacs, A. Aboltins. 2023. "The Synthetic Data Application in the UAV Recognition Systems Development", Advances in Information, Electronic and Electrical Engineering (AIEEE).
- Kaspars Sudars, Ivars Namatēvs, Jānis Judvaitis, Rihards Balašs, Artūrs Ņikuļins, Astile Peter, Sarmīte Strautiņa, Edīte Kaufmane, Ieva Kalniņa. YOLOv5 Deep Neural Network for Quince and Raspberry Detection on RGB Images
- Edīte Kaufmane, Kaspars Sudars, Ivars Namatēvs, Ieva Kalniņa, Jānis Judvaitis, Rihards Balašs, Sarmīte Strautiņa. QuinceSet: Dataset of annotated Japanese quince images for object detection
- Ivars Namatēvs, Kaspars Sudars, Artis Dobrājs. Interpretability versus Explainability: Classification for Understanding Deep Learning Systems and Models.
- Ivars Namatēvs, Roberts Kadiķis, Anatolijs Zencovs, Laura Leja, Artis Dobrājs. Dataset of Annotated Virtual Detection Line for Road Traffic Monitoring
- Martin Cech, Ared-Jan Beltman, Kaspars Ozols. Digital Twins and AI in Smart Motion Control Applications
- Laura Leja, Vitālijs Purlans, Rihards Novickis, Andrejs Cvetkovs, Kaspars Ozols. Mathematical Model and Synthetic Data Generation for Infra-Red Sensors
- Diana Duplevska, Maksims Ivanovs, Janis Arents, Roberts Kadikis. Sim2Real image translation to improve a synthetic dataset for a bin picking task
- Racinskis, Peteris, Janis Arents, and Modris Greitans. 2022. "A Motion Capture and Imitation Learning Based Approach to Robot Control" Applied Sciences 12, no. 14: 7186. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147186
- Arents, J., Lesser, B., Bizuns, A., Kadikis, R., Buls, E., Greitans, M. (2022). Synthetic Data of Randomly Piled, Similar Objects for Deep Learning-Based Object Detection. In: Sclaroff, S., Distante, C., Leo, M., Farinella, G.M., Tombari, F. (eds) Image Analysis and Processing – ICIAP 2022. ICIAP 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13232. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06430-2_59
- Torres, P.; Arents, J.; Marques, H.; Marques, P. Bin-Picking Solution for Randomly Placed Automotive Connectors Based on Machine Learning Techniques. Electronics, 2022, 11, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11030476
- Ivanovs, Maksims, Kaspars Ozols, Artis Dobrajs, and Roberts Kadikis. 2022. "Improving Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes for Self-Driving Cars with Synthetic Images" Sensors 22, no. 6: 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22062252
- Janis Arents, Modris Greitans. 2022. "Smart Industrial Robot Control Trends, Challenges and Opportunities within Manufacturing" Applied Sciences 12, no. 2: 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020937
- Sudars, Kaspars, Ivars Namatēvs, and Kaspars Ozols. 2022. "Improving Performance of the PRYSTINE Traffic Sign Classification by Using a Perturbation-Based Explainability Approach" Journal of Imaging 8, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8020030
Recent patents
Head of laboratory
Laboratory staff
Dr. sc. ing. Kaspars Ozols
Deputy director of development, Senior Researcher
+371 67558161[protected]